The Program
The Bachelor of Science in Economics Program was instituted in 1986. The program was born out of the necessity of constructing alternative development strategies for overcoming the economic crisis which beset the country during the period. These strategies required the consideration of prevailing economic concerns which included, among others, the heavy debt burden, poverty, unemployment, unproductive and inefficient industries, as well as malnutrition. Furthermore, there was a need to better
understand the impacts of natural resource exploitation and environmental degradation on the country’s development path.
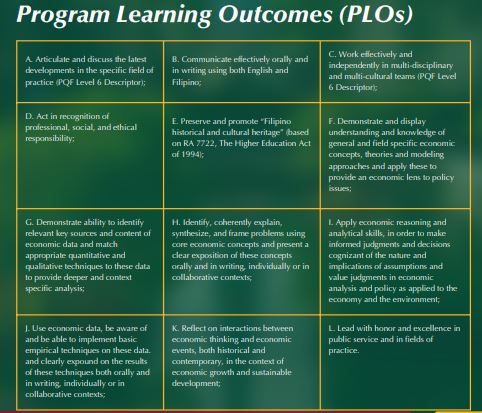
The BS Economics program aims to produce graduates who possess:
- the necessary skills in quantitative and policy analyses for teaching and research in economics;
- the ability to analyze, synthesize, and evaluate economic concepts, issues, and data relevant to policy decision- making in the public or private sector; and
- a deep appreciation of the economic issues and problems besetting the country, as well as an objective and critical attitude towards the arguments and policies meant to address them.
Specialization
- Development Economics—focuses on theories and problems of growth; developmental survey of experiences in low- income and high income countries.
- Environmental Economics—centers on the economic role of environment in growth and development.
Requirements
Students in the Program are required to complete 135 academic units, usually in about four years. The Curriculum is divided into three components:
- (a) The general education courses aim to develop well-rounded students and give exposure to the non-economic aspects of society.
- (b) Core courses provide rigorous training in economic theory and analytical tools.
- (c) Students can choose between development economics and environ-mental economics as an area of specialization.
New Freshmen are admitted directly to the program through the UP College Admission Test (UPCAT).
Career Prospects
Courses Offered
| Course Code | Description |
|---|---|
| ECON 11 | General Economics |
| ECON 101 | Intermediate Macroeconomic Theory |
| ECON 102 | Intermediate Microeconomic Theory |
| ECON 103 | Introduction to Growth Theory and Open Economy Macroeconomics |
| ECON 104 | Introduction to Factor Market Analysis, General Equilibrium and Welfare Economics |
| ECON 110 | History of Economic Doctrines |
| ECON 115 | Philippine Economic History |
| ECON 121 | Money and Banking |
| ECON 130 | Elements of Mathematical Economics |
| ECON 137 | Introduction to Econometrics |
| ECON 138 | Intermediate Econometrics |
| ECON 141 | International Economics |
| ECON 151 | Public Economics |
| ECON 170 | Environmental Economics |
| ECON 175 | Benefit Cost Analysis |
| ECON 185 | Development Economics |
| ECON 199 | Undergraduate Seminar |
| ECON 200 | Undergraduate Thesis |
| Course Code | Description |
|---|---|
| ECON 106 | Consumption Economics |
| ECON 134 | Experimental Economics |
| ECON 155 | Economics of Regulation |
| ECON 166 | Fundamentals of Energy Economics |
| ECON 172 | Economic Analysis of Pollution Control Policies |
| ECON 176 | Economics of Climate Change and Adaptation |
| ECON 181 | Human Resource Economics |
| ECON 191 | Special Topics in Financial Economics: Fundamental, Technical and Behavioral Analysis of Financial Markets (2SAY2223) |
Downloadables
- UPLB OCS Form No.105 Application for Revision in the Approved Plan of Course Work
- UPLB OCS Form No.106 Application for Substitution of Courses
- Academic Advisers as of 2nd Semester AY2022–2023
- BSECON Curriculum
- BS ECON GE Program Plan of Study (DE FORM 101)
- BS ECON Plan of Study (DE FORM 102)
- Student Form for Raising Clarifications on Class Requirement Scores and Rechecking
- List of Specialization Courses and Corresponding Prerequisite
- Program Educational Outcomes and Program Learning Outcomes of the BS Economics Program